Table of Contents
What is Fluorescent lamp?
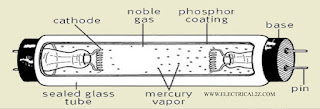
The Fluorescent lamp tube consists of a glass tube 25mm in diameter and 0.6mt, 1.2mt and 1.5 MT in length. The tube contains argon gas at a low pressure of 2.5 MT and one or two drops of mercury and inside surface of the tube is coated with a thin layer of Fluorescent material in the form of a powder.
The coating material used depends upon the color effect desired and may consist of zinc silicate, cadmium silicate or calcium tungsten. These organic chemicals are known as phosphorous which transformers short waves invisible radiation into visible light. At the start, a current is passed through filaments which get heated up and emit electrons. This is achieved by the use of choke with a starter.
The choke is connected in series with the tube which acts as ballasts in running conditions and provides a high voltage impulse or surge for starting. At the time when the switch is operated the starter is provided and the electrodes get heated and start emitting sufficient electrons. The switches or starters are of two types:
a) Thermal type starter b) Glow type starter
The bimetallic strips of the starter are normally open. When the supply is switched ON, full voltage is available across the bimetallic strips of the starter. This discharge heats the bimetallic strips of the starter causing them to bend and make contact. Now the tube filaments get heated and emit electrons inside the tube due to the flow of current.
Now the voltage across the strips of the starter is reduced to zero. Hence the bimetallic strips cool down and the contacts open. Due to the change of current, high voltage is induced in the choke e=L di/dt. The high voltage produces an arc between the filaments of the tube. Hence the mercury in the tube discharges and the tube emit light.
After the establishment of light in the tube, the voltage maintains light is reduced to 110V. As the tube current flows through the choke, sufficient voltage drop occurs in the choke. Thereby allowing only the required voltage to be applied across the tube. Also, the choke limits the current in the lamp circuit. Due to the choke, the power factor of the circuit is low. Hence to improve the power factor a capacitor is connected across the supply.
 |
| Fluorescent Lamp |
Advantages
- Efficiency and life under normal conditions are three times of those for filament lamp.
- The quality of the light obtained is much superior.
Since the stroboscopic effect is present, they are suitable for semi-direct lighting, domestic, industrial, commercial, roads and halls, etc.
What is Compact Fluorescent Lamp?
A CFL is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent light bulb. The Compact fluorescent lamp is also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light, and compact fluorescent tube. Some types of CFL fit into light fixtures designed for incandescent bulbs. Compact fluorescent light use a tube which is curved or folded to fit into the space of an incandescent bulb. A compact electronic ballast in the base of the CFL.
Compact Fluorescent Lamp Working Principle
The electrons that are bound to mercury atoms are excited to states where they will radiate ultraviolet light as they return to a lower energy level. This emitted ultraviolet light is converted into visible light as it strikes the fluorescent coating as well as into heat when absorbed by other materials.
 |
| Compact Fluorescent Lamp – CFL |
Two Main Components of Compact Fluorescent Lamp
ballast and a gas-filled tube where ballasts contain a small circuit board with a bridge rectifier, a filter capacitor and usually two switching transistors, which are often insulated-gate bipolar transistors. The incoming alternating current is first rectified to direct current and then converted to high-frequency AC by the transistors, connected as a resonant series DC to AC inverter. The resulting high frequency is applied to the CFL tube.
Since the resonant converter tends to stabilize lamp current over a range of input voltages. Lamps emit light from a mix of phosphors, each emitting one band of color with some bands still in the ultraviolet range as can be seen on the light spectrum. This is the reason why additional UV filtering, is required to reduce damage to the retina.
Compact fluorescent lamp output is roughly proportional to the phosphor surface area. Typical shapes of CFL light tubes are a helix with one or more turns, multiple parallel tubes, circular arc, or a butterfly. Lamps use three or four phosphors to achieve a pure white light with a color rendering index of about 80, where the maximum 100 represents the appearance of colors under daylight or other sources of black-body radiation such as an incandescent light bulb.
Types of Compact Fluorescent Lamp
1. Integrated
2. Non-integrated CFL
Integrated CFL
The type of lamps combines a ballast and the tube in a single unit. Integrated lamps allow peoples to replace incandescent lamps easily with CFLs. This type of CFLs works well in any standards. Incandescent lights, reducing the cost of converting to fluorescent. Dimmable models with three-way lamps with standard bases are available easily.
Non-integrated CFL
The lamps have the ballast permanently installed in the luminaries. This type of CFL housings can be both more expensive and sophisticated. There are two types of tubes available in the Non-integrated CFL are
1. A bi-pin tube designed for conventional ballast,
2. A quad-pin tube designed for electronic ballast or conventional ballast with an external starter.
Comparison of Compact Fluorescent Lamp with Incandescent Lamp
If incandescent lamps are replaced by CFLs, the heat produced due to lighting is significantly reduced. In office or buildings where A/c (air conditioning) is often required, CFLs reduce the load on the cooling system when compared to the use of incandescent lamps, resulting in savings in electricity in addition to the energy efficiency savings of the lamps themselves.
|
Compact Fluorescent Lamp
|
Incandescent Lamp
|
|
Typically have a rated service life of 6000 – 15000 hours.
|
750 to 1000 hours of service life.
|
|
Incandescent lamps giving the same amount of visible light, CFLs use one-fifth to one-third the electric power and last eight to fifteen times longer.
|
Electric power consumption is high while comparing CFLs
|
|
Its purchase price is higher than the incandescent lamp, but less electric bill charge.
|
Electric bill charge is the high but purchasing price is low.
|
|
Its radiate a spectral power distribution that is different from that of incandescent lamps
|
Improved phosphor formulations have improved the perceived color of the light emitted by CFLs, such that some sources rate the best “soft white” CFLs as subjectively similar in color to standard incandescent lamps
|
Limitations of Compact Fluorescent Lamp
- The lamps, like all fluorescent lamps, contain mercury as vapor inside the glass tubing.
- CFLs contain toxic mercury which complicates their disposal. In many countries, governments have banned the disposal of CFLs together with the regular garbage.
- Most CFLs contain 3–5 mg per bulb, with the bulbs labeled “Eco-friendly” containing as little as 1 mg.
- Because mercury is poisonous, even these small amounts are a concern for landfills and waste incinerators where the mercury from lamps may be released and contribute to air and water pollution.
- Health and environmental concerns about mercury have prompted many jurisdictions to require spent lamps to be properly disposed of or recycled, rather than being included in the general waste stream sent to landfills.
Hope you understand this article about the What is Fluorescent Lamp and CFL. In case of any doubt please comment below. Please follow our website for future updates. Thank you for visiting our website @ElectricicanWorld.Net



Thanks for sharing your knowledge!