 |
| What is Thermal Power Plant – Working and Layout of Steam Power Plant |
Thermal Power Plant is involves the conversion of heat energy into the electrical energy. In this article we are going to know about thermal power plant working, operation and layout of schematic arrangement. Arrangement cost of Steam power plant is very lower than hydro and nuclear power plant.
Table of Contents
What is Thermal Power Plant? Working principle
In a thermal power plant a steam turbine is rotated with the help of high pressure and high temperature steam by using fossil fuels and this rotation is transferred to a generator to produce electricity.
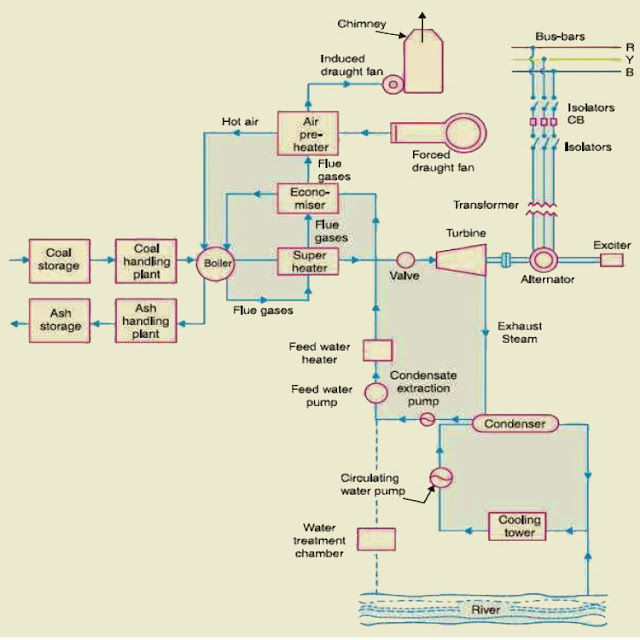
Thermal Power Plant Layout
Steam power plant simply involves the conversion of heat energy into electrical energy. The method of arrangement can be divided into the following stages,
- Coal and ash handling arrangement
- Thermal power generation
- Generating plant
- Steam turbine
- Alternator
- Feed water
- Cooling arrangement
Coal and Ash Handling Plant
The coal is transported to the energy station by road or rail and is stored in the coal storage plant. Storage of coal is primarily a matter of protection against coal strikes, failure of transportation system and general coal shortages. From the coal storage plant, coal is delivered to the coal handling plant where it is pulverized in order to increase its surface exposure, thus promoting rapid combustion without using large quantity of excess air.
The fine-grained coal is fed to the boiler by belt conveyors. The coal is burnt in the boiler and also the ash produced after the complete combustion of coal is removed to the ash handling plant and then delivered to the ash storage plant for disposal. The removal of the ash from the boiler chamber is important for correct burning of coal.
Thermal Power Generation
The thermal power generation plant consists of a boiler for the production of steam and other auxiliary equipment for the use of flue gases.
1. Boiler
The heat of combustion of coal in the boiler is used to convert water into steam at extreme temperature and pressure. The flue gases from the boiler make their journey through super-heated, economizer, air pre-heater and are finally exhausted to atmosphere through the chimney.
2. Super heater
The steam created in the boiler is wet and is passed through a super heater where it’s dried and super-heated by the flue gases on their way to chimney. Super-heating provides two principal benefits. Firstly, the overall efficiency is increased. Secondly, too much condensation in the last stages of turbine (which would cause blade corrosion) is avoided. The super-heated steam from the super heater is fed to steam turbine through the valve.
3. Economizer
An economizer is essentially a feed water heater and derives heat from the flue gases for this purpose. The feed water is fed to the economizer before supplying to the boiler. The economizer extracts a part of heat of flue gases to increase the feed water temperature.
4. Air Pre-Heater
An air pre-heater increases the temperature of the air supplied for coal burning by deriving heat from flue gases. Air is drawn from the atmosphere by a forced drought fan and is passed through air pre-heater before supplying to the boiler chamber. The air preheated extracts heat from flue gases and increases the temperature of air used for coal combustion. The principal benefits of preheating the air are increased thermal potency and raised steam capability per square meter of boiler surface.
Steam Turbine
The dry and super-heated steam from the super heater is fed to the steam turbine through main valve. The heat energy of steam once passing over the blades of steam turbine is converted into mechanical energy. After giving heat energy to the turbine, the steam is exhausted to the condenser which condenses the exhausted steam by means of cold water circulation.
Alternator
The steam turbine is coupled to an alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy of steam turbine into electrical energy. The electrical output from the alternator is delivered to the bus bars through transformer, isolators and switch gears.
Feed Water
The condensate water from the condenser is used as feed water to the boiler. Some water also could be lost in the cycle that is appropriately created up from external source. The feed water on its way to the boiler is heated by water heaters and economizer. This helps in raising the overall efficiency of the plant.
Cooling System
In order to improve the efficiency of the plant, the steam exhausted from the turbine is condensed by means of a condenser. Water is drawn from a natural source of supply like a river, lake and canal and is circulated through the condenser. The circulating water takes up the heat of the exhausted steam and itself becomes hot.
This hot water starting out from the condenser is discharged at an appropriate location down the lake. In case the availability of water from the source of supply is not assured throughout the year, cooling towers are used. During the scarcity of water in the lake, hot water from the condenser is passed on to the cooling towers where it is cooled. The cold water from the cooling tower is reused in the condenser.
Advantages of Thermal Power Station
1. Fuel cost of thermal power plant is relatively low.
2. We can produce steam energy almost every where in the world.
3. Heat production System is simple compared to other system.
4. Overall system cost effective.
5. Easy mechanism.
6. Same heat could be reused.
7. Easier Maintenance of power station.
8. Use of water is prominent here, therefore, any places with ample supply of water is a perfect location for installing a thermal power station.
9. Thermal power plant needs relatively small space to be installed.
 |
| Thermal Power Plant Layout – Comparison Between Power Plants |
Disadvantages of Thermal Power Station
1. Huge emission of Carbon-di-oxide (CO2) in the atmosphere.
2. Exhausted gases harms outside environment badly.
3. overall efficiency is low.
4. Thermal engines requires huge amount of lubricating oil that is very expensive.
5. Nuclear thermal power plant demands excessive amount of water for cooling purpose.
6. Coal type thermal power plant requires comparatively larger duration before it supply generated power to the grid.
7. This type of power station ultimately responsible for raise in sea water level.
Comparison of Thermal, Hydro and Nuclear Power Plant
|
Thermal Plant
|
Nuclear Plant
|
|
|
Located where water and coal and transportation facilities are adequate.
|
Located where large reservoirs or dams can be created like in hilly areas.
|
Located in isolated areas
away from population.
|
|
Initial cost is lower than
hydro and nuclear.
|
Initial cost pretty high
due to large dam construction.
|
Initial cost is highest as cost of reactor construction is very high.
|
|
Running cost is higher than nuclear and hydro due to amount of coal required.
|
Practically nil as no fuel is required.
|
Cost of running is low as
very very less amount of
fuel is required.
|
|
Coal is source of power.
So limited quantity is available.
|
Water is source of power which is not a dependable quantity.
|
Uranium is fuel source
along with platinum rods.
So sufficient quantity is
available.
|
|
Cost of fuel transportation
is maximum due to large
demand for coal.
|
No cost for fuel transportation.
|
Cost of fuel transportation is
minimum due to small quantity required.
|
|
Least environment friendly.
|
Most environment friendly.
|
Better friend of environment than steam power plant.
|
|
25% overall efficiency.
|
Around 85% efficient.
|
More efficient than steam
power.
|
|
Maintenance cost is very
high.
|
Maintenance cost is
quite low.
|
Maintenance cost is the
highest as highly skilled
workers are required.
|
|
Maximum standby losses as boiler still keep running even though turbine is not.
|
No standby losses.
|
Less standby losses.
|
Final Word
Hope you understand this article about the Thermal Power Plant. In case of any doubt please comment below. Please follow our website for future updates. Thank you for visiting our website – ElectricianWorld.Net