Troubleshoot The Wiring Problems
Some problems with wiring systems can be traced to the use of improper materials in the wiring devices. Therefore, the use of proper materials in the installation stage is a form of preventive maintenance, decreasing the likelihood of problems later. Shock hazards should be minimized by the dielectric strength of the material used for the molded interior walls and the individual wire pocket areas. Each molded piece has to support adjacent molded pieces to result in good resiliency and strength. Nylon seems to be the best for this job. Nylon devices withstand high impact in heavy-duty neoprene, urea, or phenolic materials.
Damage can be invisible and cause direct shorts and other hazards. Nylon also has the ability to withstand high voltages without breaking down. Tables detail the properties of materials commonly used in wiring devices.
In troubleshooting wiring problems, it is important to check that switches have been wired properly. Figure shows wiring diagrams for switches in various systems. Plugs and connectors must also be wired and grounded correctly. Figure shows the grounding systems used in connecting various plugs to a circuit.
In some troubleshooting situations, the electrician will be called upon to trace wires. Most multi-wire cables have color-coded conductors. Follow the color code to identify the same conductor at each end of the installation. When installing a wiring system, make a list of the color-coded conductors and where each terminates. This makes future troubleshooting easier.
Test for wire pairs using an ohmmeter. Short two wires together on one location and use an ohmmeter at the other end to test for continuity. Then mark with colored tape or a number label.
Chemical Resistance of Materials Commonly Used in Wiring Devices:
|
Chemical
|
Nylon
|
Melamine
|
Phenolic
|
Urea
|
Polyvinyl Chloride
|
Polycarbonate
|
Rubber
|
|
Acids
|
C
|
B
|
B
|
B
|
A
|
A
|
B
|
|
Alcohol
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
B
|
|
Caustic bases
|
A
|
B
|
B
|
B
|
A
|
C
|
C
|
|
Gasoline
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
C
|
A
|
A
|
B
|
|
Grease
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
B
|
|
Kerosene
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
Oil
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
Solvents
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
C
|
C
|
C
|
|
Water
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
B
|
A—Completely resistant; good-to-excellent, recommended for general use.
B—Resistant; fair-to-good limited service.
C—Prone to slow attack; not recommended for use.
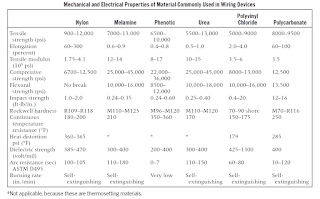 |
| Materials Commonly Used in Wiring Devices |
Final Word
Hope you understand this article about the Types and uses of How to Troubleshoot The Wiring Problems. Incase of any doubt please comment below. Subscribe our website to get every new post update to your email. Please follow our website @Electrical2z for future updates. Thank you for visiting our website.



